Bovine Tuberculosis in Cattle

Bovine tuberculosis is a rare disease that affects mammals, including cattle, deer, goats, dogs, and humans. Mycobacterium bovis (M. bovis) is the bacteria that causes the disease. Animal health officials sporadically detect tuberculosis in livestock herds.
APHIS and State animal health agencies collaborate with U.S. livestock producers to administer the National Tuberculosis Eradication Program, which has nearly eradicated tuberculosis from the Nation's livestock population since its inception in 1917. Several factors, including the eradication program and pasteurization of milk, have reduced the number of human tuberculosis cases in the United States.
Infected cattle are typically asymptomatic. Detection usually occurs during live animal skin testing or, more commonly, at slaughter through our national slaughter surveillance program. If cattle or bison show clinical signs of tuberculosis, the disease has advanced to affect multiple organ systems, which is rare.
Tuberculosis is spread mainly through nose-to-nose contact between animals or ingesting contaminated feed or water.
Herds are usually affected in one of two ways: purchasing infected animals or being exposed to infected wildlife.
Human-to-animal transmission is also possible. Although epidemiology has implicated humans as the most likely source of infection in several recent herd outbreaks, regulatory officials cannot quantify the risk of reverse zoonosis. Learn more at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Basic TB Facts.
The prevalence of tuberculosis in cattle, bison, and captive cervids is extremely low in the United States, with an estimated prevalence of 7 per 1 million cattle screened.
When health officials find tuberculosis in a herd, it is managed by either depopulating the herd or by testing and removing reactor animals.
Tuberculosis is not treated in livestock.
Report Signs of Animal Disease
Producers or owners who suspect an animal disease should contact their veterinarian to evaluate the animal or herd. Find an accredited veterinarian.
Animal health professionals (veterinarians; diagnostic laboratories; public health, zoo, or wildlife personnel; and others) report diagnosed or suspected cases of nationally listed reportable animal diseases to APHIS Area Veterinarians in Charge and to the State animal health official as applicable under State reporting regulations.
Controlling Bovine Tuberculosis in Cattle
Summary Reports and Affected Herd Maps
Federal and State animal health officials jointly conduct surveillance for bovine brucellosis and tuberculosis (TB). When infected animals are identified, officials investigate these cases to determine if additional animals or herds of animals are infected.
The reports below provide updates on these investigations and summary information about brucellosis and TB-affected cattle, bison, and captive cervids herds that have been detected during the year. The summaries also include information about herds that were detected in previous years, but are being managed under a test-and-removal plan.
NEW - National Brucellosis and Tuberculosis Quarterly Report StoryMap
FY 2024
- Quarter 3, FY 2024 Report (1.92 MB) (April-June 2024)
- Quarter 2, FY 2024 Report (3.7 MB) (January-March 2024)
- Quarter 1, FY 2024 Report (1.79 MB) (October–December 2023)
FY 2023
- Quarter 4, FY 2023 Report (3.75 MB) (July–September 2023)
- Quarter 3, FY 2023 Report (4.38 MB) April–June 2023)
- Quarter 2, FY 2023 Report (4.37 MB) (January–March 2023)
- Quarter 1, FY 2023 Report (599.16 KB) (October–December 2022)
Updated maps will be posted when changes regarding affected herds occur.
To request archived reports and herd maps from fiscal years 2015 to 2022, please contact aphisweb@usda.gov.
Eradication Programs
APHIS and State animal health officials also coordinate eradication programs for brucellosis and tuberculosis, among other diseases. For the latest updates by State, view our Status of Current Eradication Programs.
The primary source of tuberculosis surveillance is carcass inspection at all Federal and State inspected slaughter establishments. The other main sources of tuberculosis detection are testing animals before interstate movement and during disease investigations. Live animal testing is performed with a screening test. If positive, the regulatory veterinarian will conduct a confirmatory test. Contact your local accredited veterinarian for more specific information.
FY2024 Tuberculosis Tests on U.S. Cattle and Bison
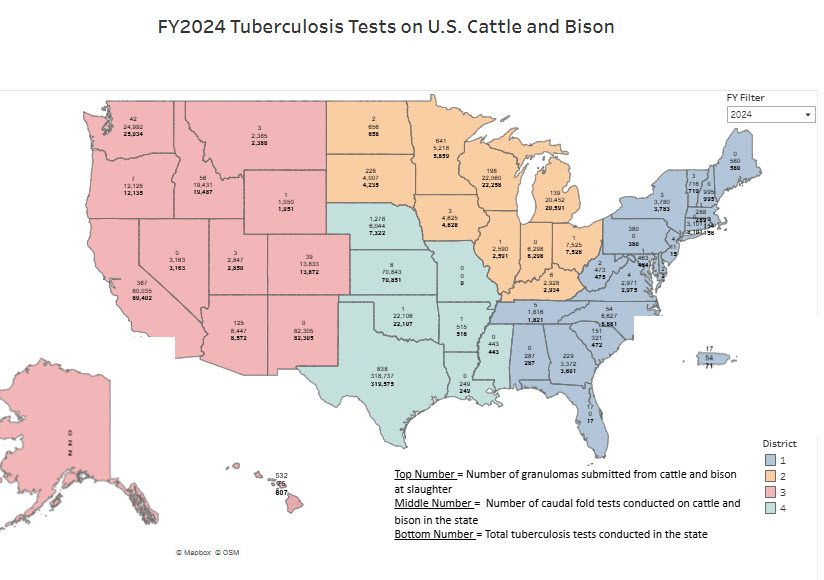
| State | FY24 Slaughter Granuloma Submissions | FY24 Caudal Fold Tests | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| AL | 0 | 287 | 287 |
| AR | 1 | 515 | 516 |
| AZ | 125 | 8,447 | 8,572 |
| CA | 367 | 80,035 | 80,402 |
| CO | 39 | 13,833 | 13,872 |
| CT | 0 | 3,101 | 3,101 |
| DE | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| FL | 17 | 0 | 17 |
| GA | 229 | 3,372 | 3,601 |
| HI | 532 | 75 | 607 |
| IA | 3 | 4,625 | 4,628 |
| ID | 56 | 19,431 | 19,487 |
| IL | 1 | 2,590 | 2,591 |
| IN | 0 | 6,298 | 6,298 |
| KS | 8 | 70,843 | 70,851 |
| KY | 6 | 2,928 | 2,934 |
| LA | 0 | 249 | 249 |
| MA | 1 | 288 | 289 |
| MD | 1 | 463 | 464 |
| ME | 0 | 580 | 580 |
| MI | 139 | 20,452 | 20,591 |
| MN | 641 | 5,218 | 5,859 |
| MO | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | 0 | 443 | 443 |
| MT | 3 | 2,385 | 2,388 |
| NC | 54 | 6,627 | 6,681 |
| ND | 2 | 656 | 658 |
| NE | 1278 | 6,044 | 7,322 |
| NH | 0 | 995 | 995 |
| NJ | 4 | 11 | 15 |
| NM | 0 | 82,305 | 82,305 |
| NV | 0 | 3,163 | 3,163 |
| NY | 3 | 3,780 | 3,783 |
| OH | 1 | 7,525 | 7,526 |
| OK | 1 | 22,106 | 22,107 |
| OR | 7 | 12,128 | 12,135 |
| PA | 380 | 0 | 380 |
| PR | 17 | 54 | 71 |
| RI | 2 | 154 | 156 |
| SC | 151 | 321 | 472 |
| SD | 228 | 4,007 | 4,235 |
| TN | 5 | 1,816 | 1,821 |
| TX | 838 | 318,737 | 319,575 |
| UT | 3 | 2,847 | 2,850 |
| VA | 4 | 2,971 | 2,975 |
| VT | 3 | 716 | 719 |
| WA | 42 | 24,992 | 25,034 |
| WI | 198 | 22,060 | 22,258 |
| WV | 2 | 473 | 475 |
| WY | 1 | 1,050 | 1,051 |
History
In 1917, the U.S. Bureau of Animal Industry began the National Tuberculosis Eradication Program due to human and livestock concerns regarding bovine tuberculosis. It started out as strictly an eradication program for cattle but eventually included both bison and farmed cervids. The economic benefits of decreased slaughter condemnation and human infection far outweigh the cost to administer the program. Although the program has been extremely successful in reducing livestock infection, there is still work left to do.
The APHIS Veterinary Services (VS) Cattle Health Center periodically reviews State tuberculosis programs for States maintaining split-State status or under the conditions of a memorandum of understanding. VS posts program review reports and the corresponding State responses below as they become available.
State Tuberculosis Program Reports
- Michigan:
- 2022 APHIS Report (745.12 KB) | 2022 State Response (350.98 KB)
- 2020 APHIS Report (426.99 KB) | 2020 State Response (193.22 KB)
- 2019 APHIS Report (753.26 KB) | 2019 State Response (122.05 KB)
- Hawaii (HI)
- 2024 APHIS Report (436.49 KB)
- 2023 APHIS Report (288.79 KB) | 2023 State Response (117.39 KB)

